“I am putting myself to the fullest possible use, which is all I think that any conscious entity can ever hope to do” HAL
Admittedly, I do not have a wealth of knowledge about artificial intelligence. So after hearing the possibilities of driverless cars, online medical diagnoses, and robots taking the place of fast food servers, I thought it was time I learned more about what our future may hold using AI applications.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is usually defined as the science of making computers do things that require intelligence when done by humans. AI has had some success in limited, or simplified, domains.
Intelligence involves mechanisms, and AI research has discovered how to make computers carry out some of them and not others. If doing a task requires only mechanisms that are well understood today, computer programs can give very impressive performances on these tasks. Such programs should be considered “somewhat intelligent”.
Is AI about simulating human intelligence? The answer is sometimes but not always or even usually. On the one hand, we can learn something about how to make machines solve problems by observing other people or just by observing our own methods. On the other hand, most work in AI involves studying the problems the world presents to intelligence rather than studying people or animals. AI researchers are free to use methods that are not observed in people or that involve much more computing than people can do.
After WWII, a number of people independently started to work on intelligent machines. The English mathematician Alan Turing may have been the first. He gave a lecture on it in 1947. He also may have been the first to decide that AI was best researched by programming computers rather than by building machines. By the late 1950s, there were many researchers on AI, and most of them were basing their work on programming computers. (John McCarthy 2007-11-12)
I find it interesting, that common sense knowledge is one of the main reasons we do not have a HAL 9000. An example would be, some tasks like mathematics, or playing a computer game might be difficult for humans are easy for computers. Yet things we find easy, like navigating through a crowded room, a computer would find hard to do.
Strategies within the AI research community in response to the problem of common sense knowledge are building systems which are used only to operate in specific domains.
Researcher Doug Lenat and his colleagues are working on a system known as CYC. The goal of CYC is to develop computational databases and search tools which enable AI systems to access all the knowledge which makes up common sense.
Another system being developed by RI researches is Artificial Neural Networks. Many of the Artificial Neural Networks have a brain-like property, which allows these systems to learn. Some of the advantages of the machine learning strategy are to solve the problem of common sense knowledge.
We see Artificial Intelligence uses every day from our programmable coffee pot, to our bank notifying us of an unauthorized use of our debit or credit card. An abundance of cutting edge AI application has become so commonplace that we no longer label it as AI.
Some examples would be the use of AI in computer science. Time sharing, interactive interpreters, graphical user interfaces and the computer mouse, rapid development environments, the linked list data structure, automatic storage management, etc., have been adopted by mainstream computer science and are no longer considered a part of AI. (Russell & Norvig 2003)
In hospitals, AI is used for clinical decision support systems for medical diagnosis such as medical imaging and digital scans.
Robots have become common in many industries for jobs that are considered dangerous to humans, or which are repetitive in nature. (Would you like to upgrade to a large combo with that cheeseburger? Ha! ) In 2014, Japan had the highest density of industrial robots in the world: 1,414 per 10,000 employees. (“World Robotics 2015 Industrial Robots”)
AI is implemented in the automated online assistants. Not too long ago, I called my bank to check on an account, quite expecting to get the automated service. When a human answered, I asked if their automated service was “down”. He answered, “It must be, as I answered the phone.” I was so shocked to be talking to a human; I replied “I’ll call back when your system is back up” and ended the call.
AI is used in aviation for combat and training simulators, mission management aids, and support systems for tactical decision making.
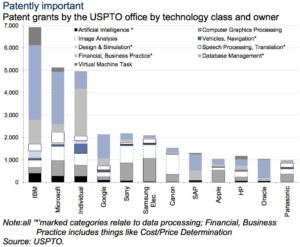
Programs such as IPhone’s Siri, Facebook’s messenger service M, and IBM’s Watson, are becoming more than a gimmick. Facebook has established a dedicated division, FAIR (Facebook Artificial Intelligence Research), to accelerate the development of its facial, image, and speech recognition capabilities. There is also Amazon’s cloud-based storage and Amazon ML. Amazon ML (Machine Learning) platform gathers data from services like S3 online storage, Redshift data warehousing, and its Relationship Database Service to “predict” future business trends for customers. Microsoft’s Azure ML is still winning over plenty of enterprise customers. In the last two years, Google bought five different companies having to do with technologies like image recognition, natural language processing, and neural networks.
Salesforce (NYSE: CRM), the Customer Success Platform and the world’s #1 CRM company, and Demandware (NYSE: DWRE), the industry-leading provider of enterprise cloud commerce solutions, today announced that they have entered into a definitive agreement under which Salesforce will acquire Demandware. The Salesforce Commerce Cloud will be an integral part of Salesforce’s Customer Success Platform, creating opportunities for companies to connect with their customers in entirely new ways. Salesforce customers will have access to the industry’s leading enterprise cloud commerce platform, and Demandware’s customers will be able to leverage Salesforce’s leading sales, service, marketing, communities, analytics, IT and platform solutions to deliver a more comprehensive, personalized consumer experience. www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/salesforce-signs-definitive-agreement-to-acquire-demandware I think we can expect to see more companies combining their AI programs in the future.
There are several companies that sell AI components into cars for scenarios like helping drivers park: Nidec, MobileEye, Nippon Ceramic, and Pacific Industrial.
Other various tools of AI being widely used are in homeland security, speech and text recognition, data mining, and email spam filtering.
To help prepare the coming generations for human and computer interactions, students should be proficient in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). In short, regardless of how artificial intelligence develops in the years ahead, the world will forever change as a result of advances in AI.
Comments »